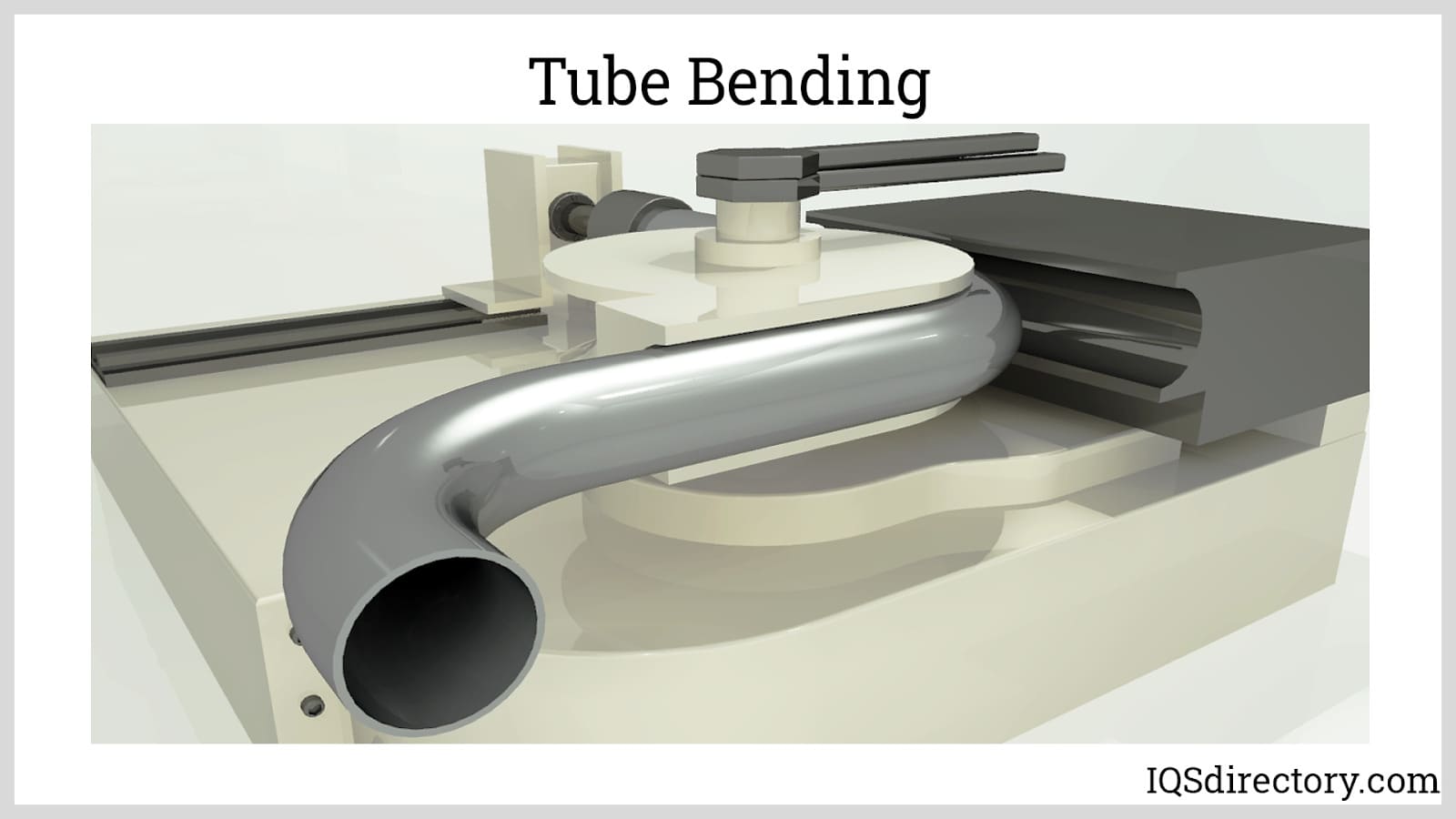
Tube benders refer to many types of electromechanical tube bending equipment. Modern tube benders help optimize manufacturing processes by minimizing production errors. A tube bending machine can handle challenging materials that are up to 1.5 times the outer diameter, have thin walls, have tight radii, or both. The tube’s cross-section is mainly preserved during the bending operation because of the bending mandrel and the counter bearing. Read More…
For 80 years Burr OAK Tool Inc. has delivered machines, tools, and expertise to the world's heat exchange manufacturers and tube processing industries. Burr OAK Tool Inc. designs and produces high quality fin dies, fin lines, tube expanders, tube cutoff machines, tube bending equipment, and coil forming units for companies in more than 75 countries.

For over 50 years, Haven Manufacturing Corporation has built a solid reputation as the productivity leader in the tube recutting industry. As our business continues to grow, we have kept the focus on providing new cost-effective machinery and total solutions that increase output without adding additional labor resources. You can trust Haven to provide fully integrated solutions to meet all of...
Universal Tube & Rollform Equipment Corp is your trusted ally in the realm of tube forming machines. Partner with us to experience a seamless integration of quality products, personalized services, and cutting-edge capabilities that redefine excellence in manufacturing solutions. Together, we can elevate your projects to new heights, ensuring that your tube forming components are not just parts...

More Tube Bending Equipment Manufacturers
Types of Tube Bending Equipment
Tube bending equipment plays a critical role in a wide variety of industrial, commercial, and manufacturing applications. Selecting the right tube bending machine or pipe bending equipment is essential for ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and productivity in processes ranging from automotive and aerospace manufacturing to HVAC, furniture, shipbuilding, and construction. Explore the different types of tube and pipe bending machines, their unique features, capabilities, and ideal applications, to help you make informed decisions tailored to your project needs.
Roll Bending Machine
The 3-roll bender, also known as a roll bending machine, is a staple in the metal forming industry for producing large-radius bends in tubes and pipes. This equipment utilizes three rollers: two fixed lower rollers and one adjustable upper roller. The tube is gradually bent as it is passed back and forth between the rollers, allowing the operator to achieve precise curvature with minimal cross-sectional distortion.
Key applications: Roll bending is ideal for fabricating handrails, structural frames, rings, arches, and other architectural or industrial components requiring smooth, sweeping curves. Its ability to handle a wide range of tube diameters and wall thicknesses makes it a versatile choice for manufacturers and fabricators.
- Minimal cross-sectional distortion
- Excellent for large-radius bends
- Common in construction, shipbuilding, and architectural metalwork

CNC Bending
CNC tube bending machines have revolutionized the pipe and tube fabrication industry by automating the bending process and delivering unparalleled accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency. These computer numerically controlled (CNC) machines use programmable presses and rollers to manipulate tubes through complex multi-axis bending operations with minimal human intervention.
Benefits of CNC bending:
- Automated for high-volume production
- Consistent, precise bends with tight tolerances
- Capable of producing intricate, multi-bend parts
- Reduced labor costs and increased throughput
Industries: CNC tube benders are indispensable in automotive, aerospace, HVAC systems, medical device manufacturing, furniture production, and more—anywhere complex or high-precision tube shapes are required.
Looking for advanced automation? Compare the best CNC tube bending machines and software solutions to streamline your manufacturing processes.

RAM Bending
RAM benders, also called press benders, are among the most basic and cost-effective tube bending machines available. These machines operate by pushing a ram or die against the tube, which is supported on either side by stationary dies. The bend radius is determined by the ram's geometry, and the spacing between dies controls the bend angle and length.
Advantages:
- Simple, robust design
- Quick setup for straightforward bends
- Low initial investment and maintenance costs
Limitations: RAM bending may cause cross-sectional distortion (e.g., ovalization) due to lack of internal support, making it less suitable for applications requiring high precision or uniformity. It is best for projects where exacting tolerances are not critical.
Common uses: Construction, plumbing, roll cages, and low-precision industrial frames.

Manual Tube Benders
Manual tube benders (or hand tube benders) are widely used for their portability, simplicity, and affordability. These devices allow operators to create bends by hand—ideal for small-scale applications, prototyping, fieldwork, and custom fabrication. Modern manual benders can handle up to 180-degree bends and are sometimes convertible to hydraulic operation for increased leverage.
Where are manual tube benders used?
- Automotive roll cages and chassis modifications
- Furniture frames and decorative metalwork
- HVAC piping, plumbing, and electrical conduit
- On-site repairs and small batch production
Decision factors: When choosing a manual tube bender, consider maximum tube diameter, material compatibility (steel, copper, aluminum, stainless steel, etc.), bend radius, and ergonomic design.
Want to know more? Explore the differences between manual and hydraulic tube benders for your specific task.

Rotary Bending Machine
The rotary draw bending machine (often referred to as a rotary bender) is the industry standard for creating precise, repeatable bends in tubes and pipes. The process involves clamping the tube securely while a bend die rotates around a fixed axis, with a pressure die guiding the tube to ensure it follows the desired radius.
Enhancements: For challenging bends, mandrels and wiper dies may be added to prevent wrinkling or warping, especially for thin-walled or large-diameter tubes.
Why choose rotary draw bending?
- High-precision, programmable bending for complex parts
- Ideal for automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing
- Capable of tight bend radii and multi-plane bends
- Reduces material waste and improves repeatability
Is rotary draw bending the best fit for your needs? Compare rotary draw bending vs. roll bending methods to determine which is right for your project.

Induction Bending Machines
Induction tube bending machines leverage electromagnetic induction to heat a localized section of the tube, making it more pliable for precise bending. The process involves drawing the tube through a die while an induction coil rapidly heats the metal at the bend point. This reduces the force required and enables tight-radius bends, even in thick-walled or large-diameter pipes.
Main advantages:
- Energy-efficient and fast bending process
- Suitable for heavy-wall, high-strength, and large-diameter tubes
- Can produce smooth bends without wrinkling or ovalization
Key applications: Induction bending is widely used in the oil and gas industry, power generation, chemical processing, shipbuilding, and infrastructure projects where robust, accurately bent pipes are required for critical systems.
Need to bend thick-walled or specialty alloys? See how induction bending compares to traditional hot bending techniques.

Vector Tube Bending
Vector tube bending machines employ advanced rotational draw technology, enabling them to produce extremely precise and complex bends through automated feeding and manipulation. With computer-controlled movement, vector benders can maintain tight tolerances and efficiently process high-strength materials.
Industries and use cases:
- Automotive exhaust and chassis components
- Aerospace hydraulic and fuel lines
- Medical device tubing and instrumentation
- Precision industrial machinery parts
Advantages: Outstanding accuracy, high repeatability, and the ability to handle intricate multi-plane bends set vector tube benders apart for advanced manufacturing needs.
Curious about vector bending vs. CNC? Discover when to use vector tube bending over traditional CNC methods.

Orbital Head Bending Machine
Orbital head bending machines utilize spinning heads and collets to bend tubes around a fixed axis. These machines can be fully automated or computer-controlled for exceptional productivity, featuring options for automated tube feeding and offloading to further streamline production lines.
Typical applications:
- Automotive components (fuel lines, brake lines)
- Air conditioning and refrigeration tubing
- Complex industrial assemblies
- High-speed, high-volume manufacturing
Key benefits: Versatility, speed, and minimal operator intervention make orbital head benders ideal for large batch production of intricate tube parts.
Want to optimize your factory for productivity? Learn how orbital head bending machines can boost your production efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Tube Bending Equipment
Selecting the optimal tube bending equipment or pipe bending machine for your operation involves evaluating several critical factors. Below, we address key questions and decision points to help you navigate your options.
- What materials will you be bending? Consider the compatibility of the machine with materials like steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, titanium, and specialty alloys.
- What tube dimensions and geometries are required? Evaluate the minimum and maximum diameters, wall thicknesses, and bend radii your workpieces demand.
- What level of precision and repeatability do you need? For tight tolerances or complex geometries, CNC and vector tube benders are optimal. For less demanding tasks, manual or RAM benders may suffice.
- What is your production volume? High-volume manufacturing benefits from automated and programmable machines (CNC, orbital, vector), while low-volume or custom work may favor manual or semi-automatic benders.
- How important is speed and automation? Automated bending equipment reduces labor costs and increases throughput.
- What is your budget? Consider both the initial investment and long-term operating costs, including maintenance, tooling, and operator training.
Still unsure which tube bender is right for you? Request a free consultation with our tube bending equipment specialists or explore our comprehensive Tube Bending FAQ for answers to common questions.
Key Benefits of Modern Tube Bending Equipment
Investing in advanced tube and pipe bending equipment yields a range of benefits for manufacturers, fabricators, and contractors, including:
- Increased accuracy and consistency: Automated machines deliver repeatable, high-quality bends that meet exact specifications.
- Greater design flexibility: Complex shapes, tight radii, and multi-plane bends are achievable with minimal setup time.
- Improved production efficiency: Automated and programmable solutions dramatically increase throughput and reduce labor costs.
- Material savings: Precision bending reduces waste and optimizes material utilization.
- Enhanced safety: Modern tube benders feature safety interlocks, guards, and ergonomic controls to protect operators.
- Scalability: From prototyping to mass production, scalable solutions accommodate business growth and changing needs.
Applications & Industries Served
The versatility of tube bending machines enables their use across multiple sectors. Common industries and applications include:
- Automotive: Exhaust systems, roll cages, chassis, brake and fuel lines
- Aerospace: Hydraulic tubing, structural supports, fuel and air systems
- HVAC & Refrigeration: Piping, heat exchangers, condenser and evaporator coils
- Furniture Manufacturing: Metal frames, chair and table legs, decorative bends
- Shipbuilding & Marine: Structural frames, handrails, piping systems
- Construction & Infrastructure: Steel frames, architectural elements, railings
- Medical Devices: Precision medical tubing, surgical instruments
- Oil & Gas, Power Generation: High-pressure piping, boiler tubes, process lines
- General Manufacturing: Custom metal fabrication, machine components
Searching for industry-specific solutions? Browse tube bending machines by application and industry to find the best equipment for your sector.
Comparing Tube Bending Equipment Manufacturers
To ensure you achieve the best results when purchasing tube bending equipment, it is essential to compare multiple tube bending equipment manufacturers and suppliers. Our tube bending equipment directory provides profiles for leading manufacturers, allowing you to:
- Review company experience and technical capabilities
- Explore product lines and supported tube dimensions
- Request quotes and technical information directly
- Preview manufacturer websites with our patented website previewer
- Send RFQs to multiple suppliers using a single, convenient form
- Evaluate after-sales support, spare parts availability, and warranty coverage
Ready to start your search? Compare top tube bending equipment manufacturers now or request a customized quote for your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions about Tube Bending Equipment
- What is the difference between tube and pipe bending?
While “tube” and “pipe” are often used interchangeably, tubes are typically measured by outside diameter and wall thickness, while pipes are measured by nominal bore and schedule. Tube bending machines are engineered to accommodate both, but it’s important to select equipment compatible with your specific material and sizing needs. - Can tube bending equipment handle stainless steel, titanium, or aluminum?
Yes, most modern tube benders are designed for a wide range of metals, but tooling and machine specifications should be matched to the material’s strength and ductility. - What is the minimum bend radius my equipment can achieve?
The minimum achievable bend radius depends on the tube material, wall thickness, and the specific bending method and tooling used. Consult manufacturer specifications for precise capabilities. - How do I maintain my tube bending equipment?
Routine maintenance includes lubrication, die inspection, software updates (for CNC systems), and periodic calibration. Refer to your equipment’s manual or contact the manufacturer for detailed maintenance schedules. - What safety considerations should I follow?
Always use personal protective equipment, follow lockout/tagout procedures, and ensure all safety guards and interlocks are in place before operation.
Have more questions? Visit our full Tube Bending FAQ or contact a tube bending expert for personalized assistance.
Get Started: Request a Quote or Consultation
Ready to upgrade your production line, expand your fabrication capabilities, or invest in new tube bending solutions? Request a quote today through our streamlined RFQ platform, or schedule a consultation with a tube bending equipment specialist. Whether you’re seeking detailed product comparisons, pricing information, or technical advice, our team is here to guide you every step of the way.
Explore, compare, and connect with leading tube bending equipment manufacturers now to find the perfect solution for your business needs.





 Automation Equipment
Automation Equipment Car Wash Equipment
Car Wash Equipment Centrifuges
Centrifuges Hydraulic Presses
Hydraulic Presses Lasers
Lasers Machinery Rebuilders
Machinery Rebuilders Paint Finishing Equipment
Paint Finishing Equipment Tube Forming Machines
Tube Forming Machines Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services